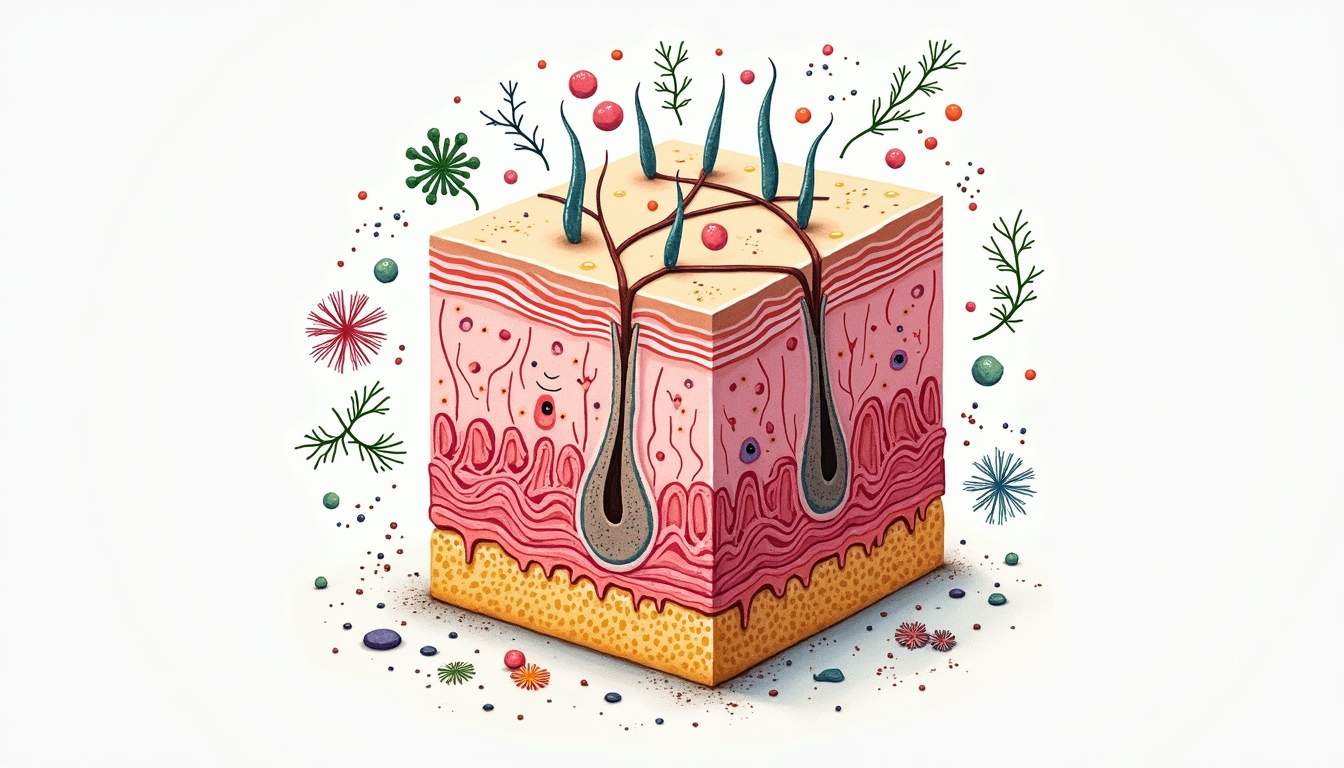
Introduction to the Skin Biome
The skin biome, also known as the skin microbiome, refers to the diverse community of microorganisms that inhabit the skin's surface. This complex ecosystem consists of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microbes that coexist with human skin cells. The skin biome plays a crucial role in maintaining skin health, protecting against pathogens, and influencing immune responses. Understanding the skin biome is essential for dermatology as it provides insights into various skin conditions and their treatments.
The skin biome is not static; it varies significantly between individuals and can be influenced by a multitude of factors including age, genetics, environment, diet, and hygiene practices. Research has shown that a balanced skin microbiome contributes to the skin's barrier function, while an imbalance, or dysbiosis, can lead to skin disorders such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis. The study of the skin biome is a rapidly evolving field, with ongoing research aimed at uncovering its complexities and implications for dermatological health.
In recent years, advancements in genomic sequencing technologies have allowed scientists to explore the skin microbiome in unprecedented detail. This has led to the identification of specific microbial species associated with healthy skin versus those linked to skin diseases. As a result, dermatologists are beginning to incorporate microbiome analysis into their clinical practice, paving the way for personalized skincare and treatment options.
The Components of the Skin Biome
Bacteria
Bacteria are the most abundant microorganisms found on the skin. They play a vital role in maintaining skin health by competing with pathogenic organisms for resources and producing antimicrobial substances. The most common bacterial genera found on healthy skin include Staphylococcus, Corynebacterium, and Propionibacterium. Each of these genera has specific functions and interactions with the skin's immune system.
For example, Staphylococcus epidermidis is a commensal bacterium that helps to protect the skin from harmful pathogens by producing antimicrobial peptides. In contrast, an overgrowth of certain bacteria, such as Cutibacterium acnes, can lead to acne development. Understanding the balance of bacterial populations on the skin is crucial for developing effective treatments for skin conditions.
Fungi
Fungi, particularly yeasts, are also integral components of the skin biome. The most well-known fungal species on the skin is Malassezia, which is associated with conditions like dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Fungi contribute to the skin's overall health by participating in the breakdown of lipids and influencing the immune response. However, an overgrowth of fungi can disrupt the skin's balance and lead to inflammatory conditions.
Viruses
Viruses, including bacteriophages, are less understood in the context of the skin biome. They can infect bacteria and influence their populations, thereby indirectly affecting the skin's health. Some studies suggest that certain viruses may play a role in skin diseases by modulating the immune response or promoting inflammation. The interaction between skin-associated viruses and other microbiome components is an area of active research.
Factors Influencing the Skin Biome
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in shaping an individual's skin biome. Genetic predispositions can influence the types of microorganisms that colonize the skin, as well as the skin's immune response to these microbes. For instance, individuals with certain genetic markers may be more susceptible to skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis due to an imbalance in their skin microbiome.
Environmental Factors
The environment significantly impacts the skin biome. Factors such as climate, pollution, and exposure to sunlight can alter the composition of the skin microbiome. For example, individuals living in urban areas with high pollution levels may experience a different microbial diversity compared to those in rural settings. Additionally, seasonal changes can affect skin moisture levels and microbial populations, leading to variations in skin health throughout the year.
Diet and Lifestyle
Diet and lifestyle choices also play a crucial role in shaping the skin biome. A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and healthy fats can promote a balanced microbiome, while processed foods and high sugar intake may contribute to dysbiosis. Furthermore, lifestyle factors such as stress, sleep patterns, and hygiene practices can influence the skin's microbial diversity and overall health.
Skin Biome and Skin Conditions
Acne
Acne is a common skin condition characterized by the presence of pimples, blackheads, and cysts. Research has shown that an imbalance in the skin microbiome, particularly an overgrowth of Cutibacterium acnes, is a significant factor in acne development. This bacterium thrives in oily environments and can trigger inflammation, leading to the characteristic lesions of acne. Understanding the role of the skin biome in acne has led to new treatment approaches, including probiotics and topical formulations aimed at restoring microbial balance.
Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition often associated with a disrupted skin barrier and altered microbiome. Studies have shown that individuals with eczema may have reduced diversity in their skin microbiome, with an overrepresentation of Staphylococcus aureus, a pathogenic bacterium. This dysbiosis can exacerbate inflammation and contribute to the symptoms of eczema. Therapeutic strategies focusing on restoring the skin microbiome are being explored as potential treatments for eczema.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin condition characterized by red, scaly patches. Recent research has indicated that the skin microbiome may play a role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Alterations in microbial diversity and the presence of specific bacterial species have been observed in individuals with psoriasis. Understanding these microbial changes may lead to novel therapeutic approaches, including the use of microbiome-modulating treatments to alleviate symptoms and improve skin health.
Maintaining a Healthy Skin Biome
Skincare Practices
Maintaining a healthy skin biome requires a balanced approach to skincare. Gentle cleansing with mild, pH-balanced products can help preserve the skin's natural microbial diversity. Avoiding harsh soaps and excessive scrubbing is essential to prevent disruption of the skin barrier and the microbiome. Additionally, incorporating moisturizers that support the skin's natural lipid barrier can promote a healthy environment for beneficial microbes.
Dietary Considerations
A diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, can support a balanced skin microbiome. Foods high in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can benefit skin health. Probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt and fermented products, may also contribute to a healthier skin microbiome by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria.
Limitations of Antibiotics
While antibiotics can be effective in treating certain skin infections, their overuse can lead to dysbiosis and negatively impact the skin biome. It is essential to use antibiotics judiciously and consider alternative treatments that target specific pathogens without disrupting the overall microbial balance. Dermatologists are increasingly aware of the importance of preserving the skin microbiome when prescribing treatments.
Future Directions in Skin Biome Research
Personalized Skincare
The future of dermatology may see a shift towards personalized skincare based on individual skin biome profiles. Advances in microbiome analysis will allow dermatologists to tailor treatments and skincare regimens to the specific needs of each patient. This personalized approach could lead to more effective management of skin conditions and improved overall skin health.
Microbiome Therapies
Research into microbiome therapies is an exciting frontier in dermatology. Probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics are being investigated for their potential to restore balance to the skin microbiome and improve skin health. Clinical trials are underway to evaluate the efficacy of these therapies in treating various skin conditions, with promising results emerging.
Education and Awareness
As our understanding of the skin biome continues to grow, educating patients and healthcare providers about its importance will be crucial. Increased awareness can lead to better skincare practices and informed decision-making regarding treatments. Dermatologists will play a vital role in disseminating this knowledge and advocating for microbiome-friendly approaches in skincare.
Conclusion
The skin biome is a complex and dynamic ecosystem that plays a critical role in skin health and disease. Understanding its components, influencing factors, and implications for skin conditions is essential for advancing dermatological care. As research in this field progresses, we can expect to see innovative treatments and personalized approaches that harness the power of the skin microbiome to enhance skin health and overall well-being.
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology