Introduction to Acne
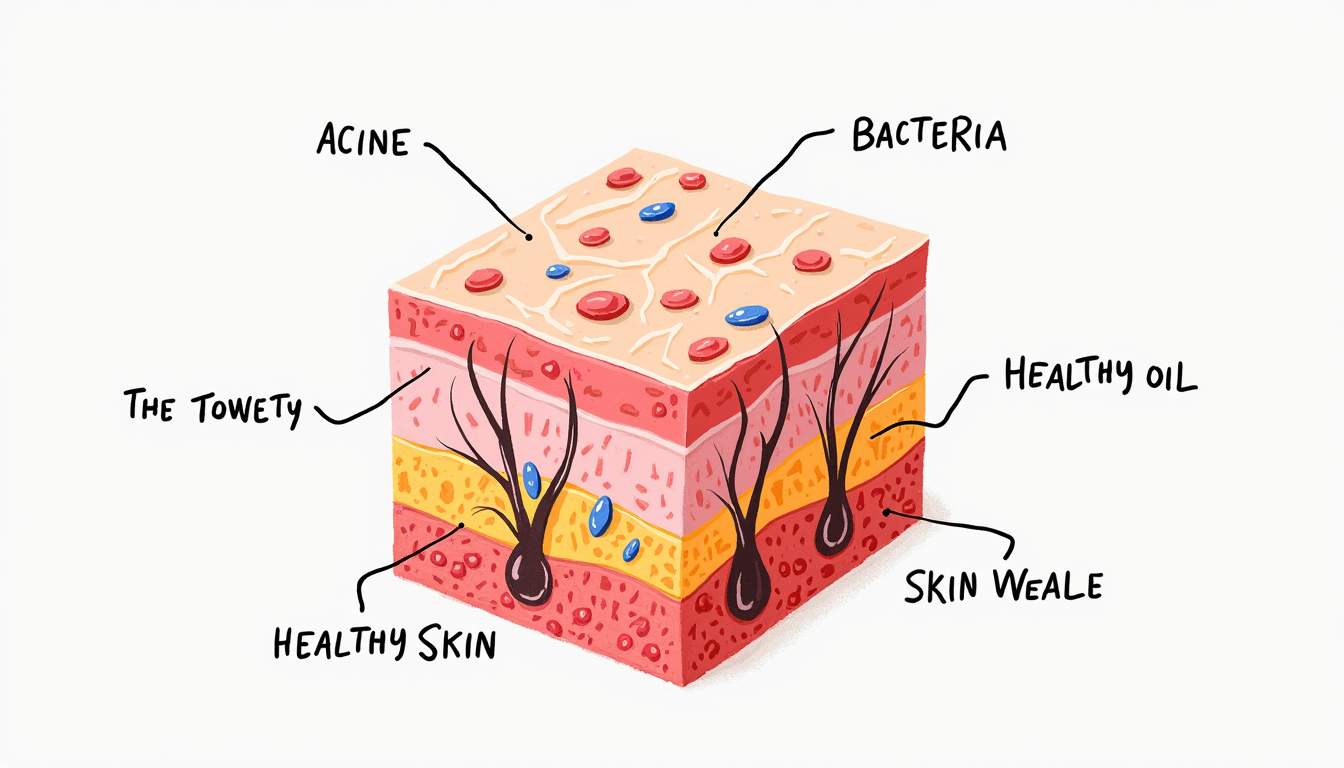
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, transcending age, gender, and ethnicity. It is primarily characterized by the presence of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts, which can occur on various parts of the body, including the face, back, shoulders, and chest. The condition arises when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to inflammation and bacterial growth. Understanding acne requires a comprehensive exploration of its causes, types, symptoms, and treatment options.
Acne is often associated with adolescence due to hormonal changes that stimulate oil production in the skin. However, it can persist into adulthood or even begin later in life, making it a significant dermatological concern. The psychological impact of acne can be profound, affecting self-esteem and quality of life. Therefore, effective management and treatment are crucial for those affected by this condition.
Types of Acne
Acne can be classified into several types based on its appearance and severity. Understanding these types is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment.
1. Non-Inflammatory Acne
Non-inflammatory acne includes comedones, which are the primary lesions of acne. They are categorized into two types:
- Open Comedones (Blackheads): These are small, dark lesions that occur when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells. The dark color is not due to dirt but rather the oxidation of melanin in the clogged follicle.
- Closed Comedones (Whiteheads): These appear as small, flesh-colored or white bumps. They occur when the follicle is completely blocked, preventing the contents from being exposed to air and oxidizing.
2. Inflammatory Acne
Inflammatory acne is characterized by redness, swelling, and pain. It includes:
- Papules: These are small, raised, red bumps that occur when the walls of the clogged follicle become inflamed.
- Pustules: Similar to papules, pustules are filled with pus and appear as red bumps with a white or yellow center.
- Nodules: These are larger, painful lesions that develop deep within the skin. They can cause significant discomfort and may lead to scarring.
- Cysts: Cystic acne is the most severe form of acne, characterized by large, painful, pus-filled lumps beneath the skin. Cysts can lead to scarring and require medical intervention.
Causes of Acne
The development of acne is multifactorial, involving a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
1. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and hormonal disorders, can significantly impact oil production in the skin. Increased levels of androgens, such as testosterone, stimulate sebaceous glands, leading to excess sebum production and clogged pores.
2. Genetics
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of acne. Individuals with a family history of acne are more likely to experience the condition themselves. Genetic factors can influence skin type, oil production, and the inflammatory response to bacteria.
3. Bacterial Growth
The skin is home to various bacteria, including Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), which can proliferate in clogged pores. This bacterial overgrowth can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to the formation of pustules and cysts.
4. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as humidity, pollution, and exposure to certain chemicals can exacerbate acne. Additionally, lifestyle choices, including diet, stress levels, and skincare routines, can influence the severity of the condition.
Symptoms of Acne
Acne symptoms can vary widely among individuals, depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Presence of Lesions: The most visible symptom of acne is the appearance of various types of lesions, including blackheads, whiteheads, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
- Redness and Inflammation: Inflammatory acne lesions often exhibit redness and swelling, indicating an active inflammatory response.
- Pain or Tenderness: Some acne lesions, particularly nodules and cysts, can be painful to the touch and may cause discomfort.
- Scarring: Severe acne can lead to scarring, which may be permanent and affect an individual’s appearance and self-esteem.
Diagnosis of Acne
Diagnosing acne typically involves a thorough clinical evaluation by a dermatologist. The dermatologist will assess the patient's medical history, family history, and the characteristics of the acne lesions. In some cases, additional tests may be conducted to rule out underlying hormonal disorders or other skin conditions.
1. Clinical Examination
During a clinical examination, the dermatologist will evaluate the type, distribution, and severity of acne lesions. This assessment helps determine the most appropriate treatment plan. The dermatologist may also inquire about the patient's skincare routine, lifestyle factors, and any previous treatments that have been attempted.
2. Hormonal Evaluation
For women experiencing adult-onset acne or those with irregular menstrual cycles, hormonal evaluation may be necessary. Blood tests can assess hormone levels and identify any underlying hormonal imbalances that may be contributing to acne.
Treatment Options for Acne
Effective acne treatment often requires a multifaceted approach, combining topical and systemic therapies tailored to the individual’s specific needs. Treatment options may include:
1. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against acne. These include:
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, retinoids help unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and promote skin cell turnover. Common examples include tretinoin and adapalene.
- Benzoyl Peroxide: This topical agent has antibacterial properties and helps reduce inflammation. It is effective against P. acnes and can be found in various over-the-counter products.
- Salicylic Acid: A beta-hydroxy acid that exfoliates the skin and helps unclog pores. It is often used in cleansers and spot treatments.
- Antibiotics: Topical antibiotics, such as clindamycin and erythromycin, can help reduce bacterial growth and inflammation.
2. Oral Medications
For moderate to severe acne, oral medications may be necessary. These include:
- Oral Antibiotics: Medications such as doxycycline and minocycline can help reduce inflammation and bacterial growth in more severe cases.
- Hormonal Treatments: For women, hormonal therapies such as oral contraceptives can help regulate hormones and reduce acne.
- Isotretinoin: A powerful oral retinoid used for severe, cystic acne that has not responded to other treatments. It requires close monitoring due to potential side effects.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in managing acne. Recommendations may include:
- Dietary Changes: Some studies suggest that high-glycemic foods and dairy products may exacerbate acne. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains may help improve skin health.
- Stress Management: Stress can trigger hormonal changes that worsen acne. Techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and regular exercise can help manage stress levels.
- Skincare Routine: Using non-comedogenic skincare products and maintaining a consistent skincare routine can help prevent clogged pores and reduce acne flare-ups.
Conclusion
Acne is a complex dermatological condition that requires a thorough understanding of its types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options. While it is often seen as a mere cosmetic issue, the psychological and emotional impact of acne can be profound. Therefore, it is essential for individuals affected by acne to seek professional guidance from dermatologists to develop effective treatment plans tailored to their specific needs. With the right approach, acne can be managed effectively, allowing individuals to regain their confidence and improve their quality of life.
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology