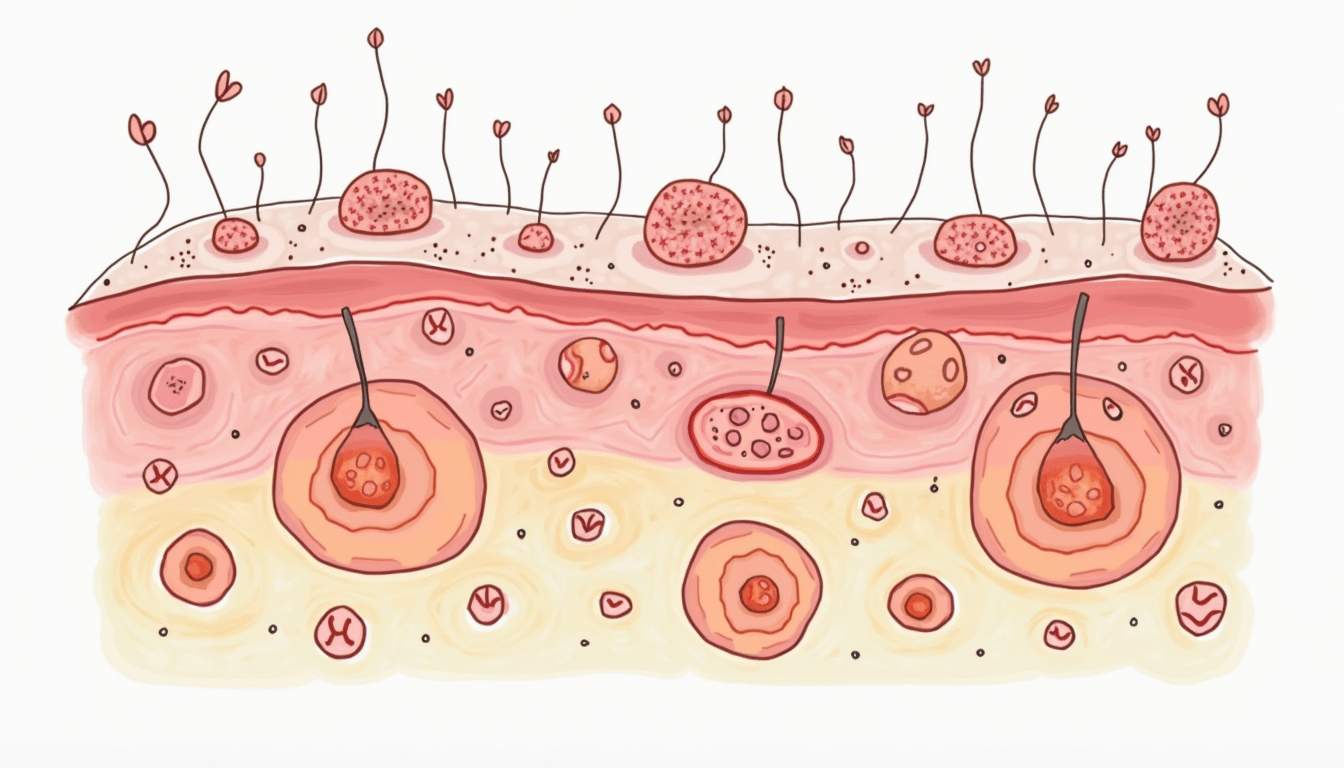
Definition of Pustules
Pustules are small, inflamed, pus-filled lesions that appear on the skin's surface. They are typically characterized by a raised, red base and a white or yellow center, which is the pus. Pustules can vary in size and are often associated with various dermatological conditions, including acne, folliculitis, and certain infections. Understanding the nature of pustules is crucial for both diagnosis and treatment in dermatology.
The presence of pustules indicates an inflammatory response in the skin, often due to infection or irritation. They can be painful or itchy, depending on the underlying cause. Pustules are commonly found on the face, back, shoulders, and arms, but can appear anywhere on the body. Their formation is often a result of the body's immune response to pathogens or irritants.
In dermatology, pustules are classified based on their characteristics and the conditions they are associated with. Recognizing the specific type of pustule can help healthcare providers determine the appropriate treatment and management strategies for patients.
Causes of Pustules
Pustules can arise from a variety of causes, each linked to different dermatological conditions. The most common causes include bacterial infections, inflammatory skin disorders, and reactions to irritants or allergens. Understanding these causes is essential for effective treatment and prevention.
Bacterial Infections
One of the primary causes of pustules is bacterial infections, particularly those caused by Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium can invade hair follicles, leading to folliculitis, which manifests as pustules around the hair shafts. In more severe cases, these infections can lead to abscess formation, which may require drainage and antibiotic treatment.
Inflammatory Skin Disorders
Inflammatory skin disorders such as acne vulgaris are also significant contributors to pustule formation. In acne, the combination of excess sebum production, clogged pores, and bacterial proliferation leads to the development of pustules. Hormonal changes, stress, and diet can exacerbate these conditions, leading to more severe outbreaks.
Allergic Reactions and Irritants
Pustules can also result from allergic reactions to certain substances, such as cosmetics, soaps, or medications. Contact dermatitis, for example, can cause pustular eruptions when the skin reacts to an allergen. Additionally, irritants like harsh chemicals or excessive friction can lead to pustule formation as the skin becomes inflamed and damaged.
Types of Pustules
Dermatologists categorize pustules into several types based on their appearance, location, and associated conditions. Recognizing these types can aid in diagnosis and treatment. Below are some common types of pustules encountered in dermatology.
Acne Pustules
Acne pustules are perhaps the most recognized form of pustules. They typically occur in adolescents and young adults due to hormonal changes that increase oil production in the skin. These pustules can be painful and often leave behind scars if not treated properly. They are usually treated with topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, or oral antibiotics in more severe cases.
Follicular Pustules
Follicular pustules are small, raised lesions that occur around hair follicles. They are often associated with folliculitis, an infection or inflammation of the hair follicles. Treatment may involve topical antibiotics or antifungal medications, depending on the underlying cause.
Impetigo Pustules
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that leads to the formation of pustules, particularly in children. These pustules can rupture, forming honey-colored crusts. Treatment typically involves topical or oral antibiotics to eradicate the infection and prevent its spread.
Other Types
Other less common types of pustules include those associated with conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and certain drug reactions. Each type requires specific diagnostic approaches and treatment plans tailored to the individual patient's needs.
Diagnosis of Pustules
Diagnosing pustules involves a thorough clinical evaluation, including a detailed patient history and physical examination. Dermatologists often assess the characteristics of the pustules, their distribution, and any associated symptoms to determine the underlying cause.
Clinical Examination
During a clinical examination, dermatologists look for specific features such as the size, color, and number of pustules, as well as the presence of other skin lesions. They may also inquire about the patient's medical history, including any recent illnesses, medications, or exposure to irritants or allergens.
Laboratory Tests
In some cases, laboratory tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. These tests can include skin cultures to identify bacterial pathogens, allergy testing to determine sensitivities, or skin biopsies to rule out other dermatological conditions. The results of these tests can provide valuable insights into the most effective treatment options.
Treatment Options for Pustules
Treatment for pustules varies widely depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Dermatologists often employ a combination of topical and systemic therapies to manage pustules effectively.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are commonly used for localized pustules. These may include:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: An antibacterial agent that helps reduce inflammation and kill bacteria associated with acne.
- Topical Antibiotics: Such as clindamycin or erythromycin, which can help reduce bacterial load on the skin.
- Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives promote cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.
Systemic Treatments
For more severe cases, systemic treatments may be necessary. These can include:
- Oral Antibiotics: Such as doxycycline or minocycline, which are effective in treating inflammatory acne and other bacterial infections.
- Hormonal Therapies: Such as oral contraceptives, which can help regulate hormonal fluctuations that contribute to acne.
- Isotretinoin: A potent retinoid used for severe acne that has not responded to other treatments.
Prevention of Pustules
Preventing pustules involves a combination of good skincare practices, lifestyle modifications, and awareness of triggers. By adopting preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing pustules and maintain healthier skin.
Skincare Routine
Establishing a consistent skincare routine is essential for preventing pustules. This should include:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild cleanser to remove excess oil and dirt without irritating the skin.
- Moisturizing: Even oily skin needs hydration. Use non-comedogenic moisturizers to avoid clogging pores.
- Sun Protection: Apply sunscreen daily to protect the skin from UV damage, which can exacerbate inflammation.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to a good skincare routine, lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in preventing pustules. These may include:
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote overall skin health.
- Stress Management: Stress can trigger hormonal changes that lead to acne. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or regular exercise can help manage stress levels.
- Avoiding Irritants: Be mindful of products that may irritate the skin, such as harsh soaps, fragrances, or certain fabrics.
Conclusion
Pustules are a common dermatological issue that can arise from various causes, including infections, inflammatory conditions, and allergic reactions. Understanding the nature of pustules, their causes, types, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention strategies is essential for effective management. By working closely with a dermatologist, individuals can develop personalized treatment plans to address their specific skin concerns and maintain healthy skin.
As research in dermatology continues to evolve, new treatments and insights into the management of pustules are likely to emerge. Staying informed about these developments can empower individuals to take charge of their skin health and seek timely intervention when necessary.
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology