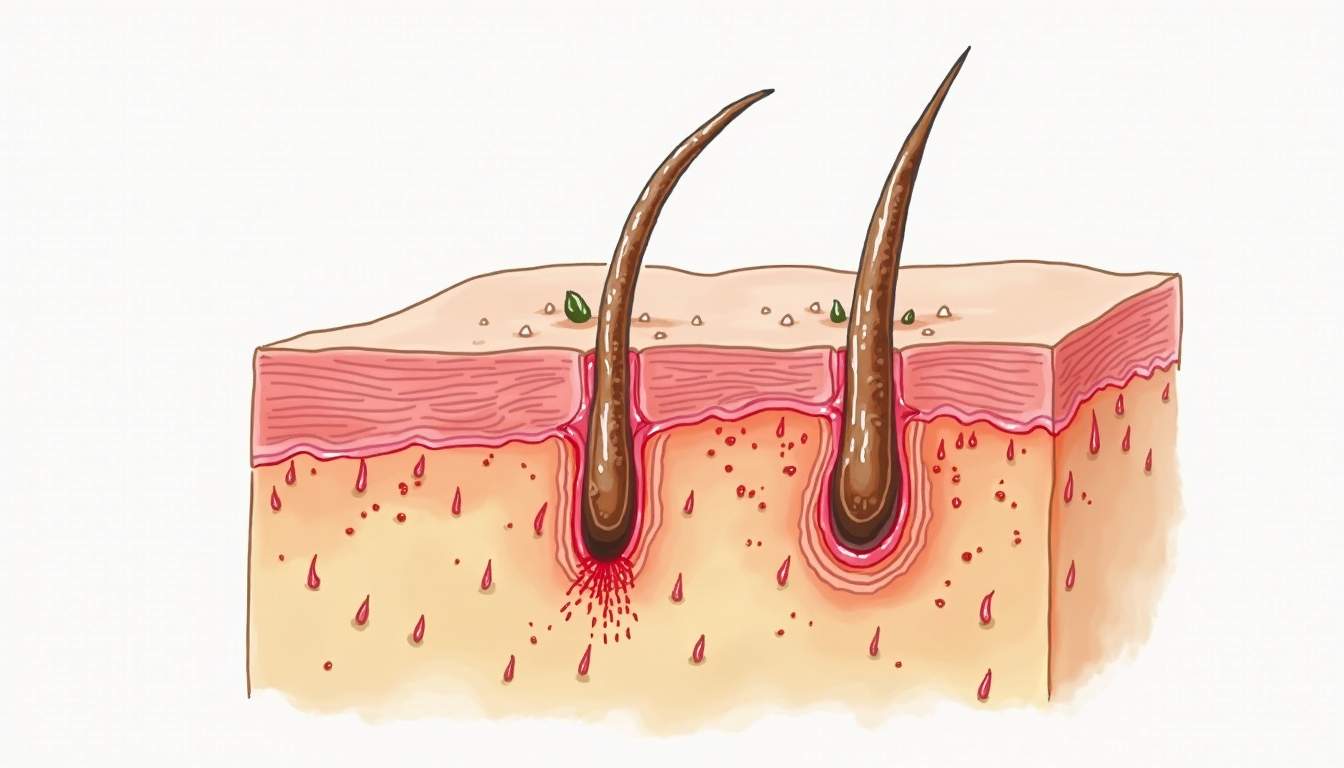
Definition of Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a common skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles. It can occur anywhere on the body where hair follicles are present, including the scalp, face, arms, legs, and buttocks. The condition is often caused by bacterial, fungal, or viral infections, and it can manifest in various forms, ranging from mild irritation to severe outbreaks. Understanding the underlying causes and symptoms of folliculitis is crucial for effective management and treatment.
The inflammation in folliculitis typically presents as small, red bumps or pustules that may resemble acne. These bumps can be itchy and painful, and they may sometimes ooze or crust over. While folliculitis is generally not a serious health threat, it can lead to discomfort and may result in scarring or pigmentation changes if left untreated. Therefore, recognizing the signs early and seeking appropriate care is essential for maintaining skin health.
Folliculitis can affect individuals of all ages and skin types, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing this condition. These factors include excessive sweating, wearing tight clothing, shaving or waxing, and having a compromised immune system. By understanding the definition and implications of folliculitis, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage the condition effectively.
Types of Folliculitis
Folliculitis can be classified into several types based on the causative agent and the clinical presentation. Each type has distinct characteristics and may require different approaches to treatment. The most common types include:
- Bacterial Folliculitis: This is the most prevalent form of folliculitis, primarily caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. It often occurs after shaving or in areas where hair follicles are irritated.
- Fungal Folliculitis: Caused by fungal infections, particularly from organisms like Malassezia, this type is more common in individuals with oily skin or those who use topical oils.
- Viral Folliculitis: This type is less common and can be associated with viral infections such as herpes simplex virus. It may present with vesicular lesions around hair follicles.
- Non-infectious Folliculitis: This form is not caused by an infection but rather results from irritation or blockage of hair follicles due to factors such as friction, chemicals, or allergic reactions.
Understanding the different types of folliculitis is vital for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Each type may have unique triggers and symptoms, necessitating tailored therapeutic approaches. For instance, bacterial folliculitis may respond well to topical antibiotics, while fungal folliculitis may require antifungal treatments. A dermatologist can help identify the specific type of folliculitis and recommend the most effective management strategies.
Causes of Folliculitis
The causes of folliculitis can be diverse, ranging from infectious agents to non-infectious irritants. Identifying the root cause is essential for effective treatment and prevention. The following are some of the primary causes of folliculitis:
Infectious Causes
Infectious agents are among the most common causes of folliculitis. Bacterial infections, particularly those caused by Staphylococcus aureus, can occur when bacteria enter the hair follicles through small cuts or abrasions. This type of folliculitis is often exacerbated by activities that irritate the skin, such as shaving or wearing tight clothing.
Fungal infections, particularly those caused by Malassezia, can also lead to folliculitis. This type is often seen in individuals with oily skin or those who use heavy topical products. Additionally, certain medications, such as antibiotics, can disrupt the natural balance of skin flora, making individuals more susceptible to fungal infections.
Non-Infectious Causes
Non-infectious causes of folliculitis can include physical irritation from friction, such as from tight clothing or shaving. Chemical irritants, such as those found in certain skincare products or hair removal treatments, can also lead to inflammation of the hair follicles. Allergic reactions to products or substances can further exacerbate the condition, leading to redness and swelling.
Other contributing factors include excessive sweating, which can create a moist environment conducive to bacterial and fungal growth, and a compromised immune system, which may hinder the body's ability to fight off infections. Understanding these causes can help individuals take preventive measures to reduce their risk of developing folliculitis.
Symptoms of Folliculitis
The symptoms of folliculitis can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Red Bumps: The most noticeable symptom is the appearance of small, red bumps or pustules around hair follicles. These may be tender to the touch and can vary in size.
- Itching and Discomfort: Many individuals experience itching or a burning sensation in the affected areas, which can lead to scratching and further irritation.
- Oozing or Crusting: In more severe cases, the bumps may ooze pus or fluid, leading to crusting over the lesions.
- Scarring: If left untreated, folliculitis can result in scarring or changes in skin pigmentation, particularly in individuals with darker skin tones.
Recognizing these symptoms early is crucial for effective management. If symptoms persist or worsen, it is advisable to seek medical attention from a dermatologist, who can provide a comprehensive evaluation and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Diagnosis of Folliculitis
Diagnosing folliculitis typically involves a thorough evaluation by a dermatologist. The process may include a detailed medical history, physical examination, and, in some cases, laboratory tests. The following steps are commonly involved in the diagnostic process:
Medical History
The dermatologist will begin by asking about the patient's medical history, including any previous skin conditions, recent skin irritations, and lifestyle factors that may contribute to folliculitis. This information helps to identify potential triggers and underlying causes.
Physical Examination
A physical examination of the affected areas is conducted to assess the appearance and distribution of the lesions. The dermatologist will look for characteristic signs of folliculitis, such as redness, swelling, and the presence of pustules or crusting.
Laboratory Tests
In some cases, laboratory tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis or identify the causative agent. This may involve taking a sample of the affected skin or pus for culture and sensitivity testing. Such tests can help determine whether the folliculitis is caused by bacteria, fungi, or other pathogens, guiding appropriate treatment decisions.
Treatment Options for Folliculitis
Treatment for folliculitis depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual patient factors. The following are common treatment options:
Topical Treatments
For mild cases of folliculitis, topical treatments may be effective. These can include:
- Antibiotic Creams: Topical antibiotics, such as mupirocin, can help combat bacterial infections.
- Antifungal Creams: In cases of fungal folliculitis, antifungal creams like clotrimazole may be prescribed.
- Corticosteroid Creams: These can help reduce inflammation and itching associated with folliculitis.
Oral Medications
For more severe or persistent cases, oral medications may be necessary. These can include:
- Oral Antibiotics: Medications such as cephalexin or doxycycline may be prescribed for bacterial folliculitis.
- Oral Antifungals: In cases of extensive fungal infections, oral antifungal medications like fluconazole may be indicated.
Preventive Measures
Preventive measures play a crucial role in managing folliculitis and reducing the risk of recurrence. These can include:
- Avoiding tight clothing that may cause friction against the skin.
- Practicing good hygiene, including regular washing of the skin and hair.
- Using non-comedogenic skincare products to minimize pore blockage.
- Avoiding shaving or waxing in areas prone to folliculitis, or using proper techniques and tools to minimize irritation.
Complications of Folliculitis
While folliculitis is generally a benign condition, it can lead to complications if not managed appropriately. Some potential complications include:
Scarring
Persistent or severe folliculitis can result in scarring, particularly if the lesions are scratched or improperly treated. Scarring can lead to long-term changes in skin texture and pigmentation, which may require further dermatological intervention for correction.
Recurrence
Individuals with a history of folliculitis may experience recurrent episodes, particularly if underlying risk factors are not addressed. Recurrence can lead to frustration and discomfort, necessitating ongoing management strategies.
Secondary Infections
Scratching or picking at folliculitis lesions can introduce additional bacteria, leading to secondary infections. These infections can complicate the treatment process and may require more aggressive interventions.
Conclusion
Folliculitis is a common dermatological condition that can cause discomfort and distress for those affected. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effective management. By recognizing the signs early and seeking appropriate care, individuals can take proactive steps to address folliculitis and maintain healthy skin. With the right approach, most cases of folliculitis can be effectively treated, allowing individuals to enjoy clear and comfortable skin.
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology