Dermal Papillae: Dermatology Explained
Small, finger-like projections of the dermis that extend into the epidermis, increasing surface area for nutrient exchange, housing capillaries and nerve endings, and contributing to skin strength and fingerprint formation.
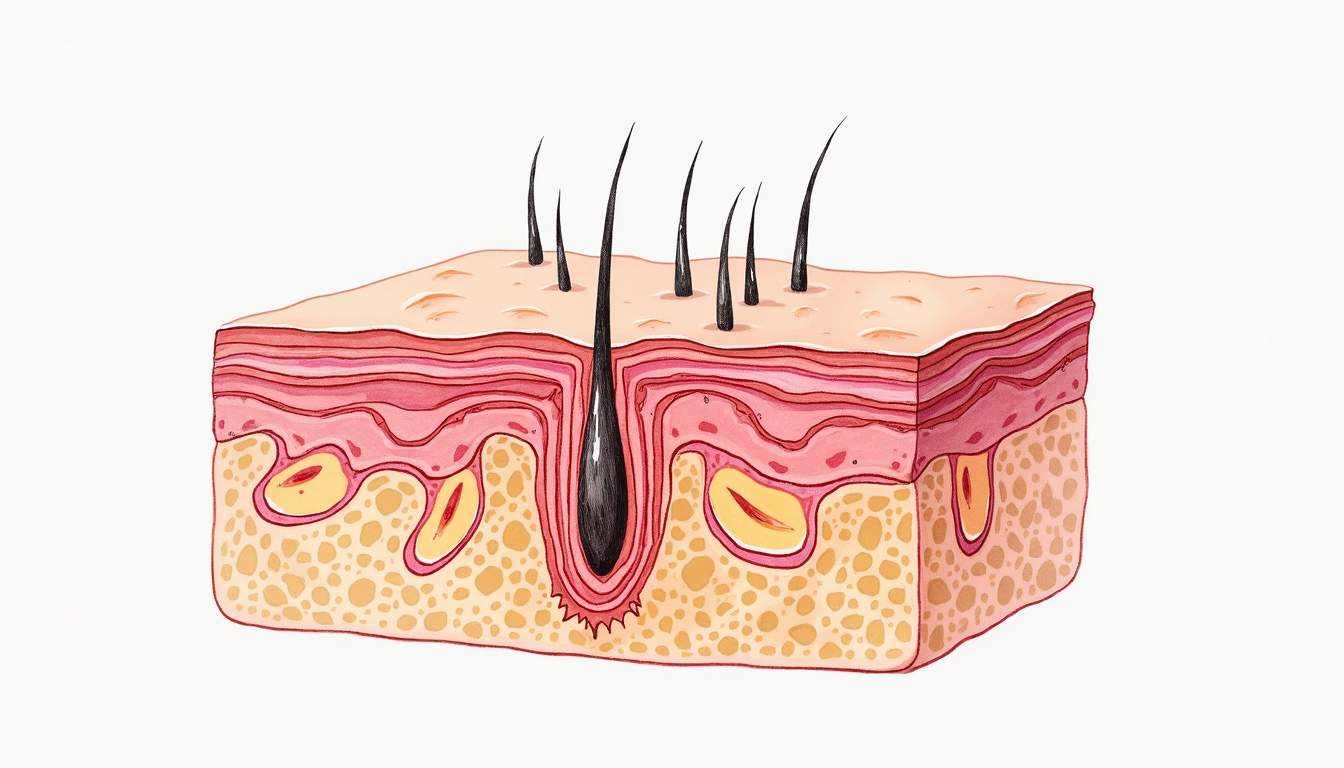
Introduction to Dermal Papillae
The dermal papillae are small, nipple-like projections found in the upper layer of the dermis, which is the second layer of skin situated beneath the epidermis. These structures play a crucial role in the overall health and functionality of the skin. They are primarily responsible for anchoring the epidermis to the dermis and facilitating the exchange of nutrients and waste products between these two layers. The dermal papillae also contain a rich supply of blood vessels and nerve endings, making them vital for the skin's sensory functions.
Understanding the structure and function of dermal papillae is essential for dermatologists and medical professionals as they navigate various skin conditions and treatments. The health of dermal papillae can significantly influence hair growth, skin elasticity, and overall skin vitality. In this glossary entry, we will explore the anatomy, functions, and clinical significance of dermal papillae in detail.
Anatomy of Dermal Papillae
Structure
Dermal papillae are composed of loose connective tissue and are characterized by their finger-like projections that extend into the epidermis. These projections increase the surface area between the dermis and epidermis, enhancing the adhesion between the two layers. Each dermal papilla contains a network of capillaries that supply oxygen and nutrients to the overlying epidermal cells, which are avascular and rely on diffusion for sustenance.
In addition to blood vessels, dermal papillae are rich in sensory nerve endings, which are responsible for the skin's tactile sensations. These nerve endings allow for the perception of touch, pressure, and temperature, making dermal papillae integral to the skin's sensory functions. The distribution and density of dermal papillae can vary across different regions of the body, contributing to the variations in skin sensitivity and texture.
Types of Dermal Papillae
Dermal papillae can be classified into two main types based on their morphology: looped and whorled. Looped dermal papillae are characterized by their elongated shape and are often found in areas of the skin that require a high degree of sensitivity, such as the fingertips. Whorled dermal papillae, on the other hand, have a more circular or spiral shape and are typically found in regions where the skin experiences less tactile stimulation.
The specific arrangement and type of dermal papillae can influence the overall texture and appearance of the skin. For instance, the presence of more pronounced dermal papillae can lead to a more textured skin surface, while flatter papillae may result in smoother skin. This variation is particularly evident in the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, where the skin is thicker and more resilient.
Functions of Dermal Papillae
Support and Nourishment
One of the primary functions of dermal papillae is to provide structural support to the epidermis. By anchoring the epidermis to the dermis, dermal papillae help maintain the integrity of the skin and prevent detachment. This structural support is essential for the overall health of the skin, as it allows for the proper functioning of various skin cells, including keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Langerhans cells.
Additionally, dermal papillae play a crucial role in nourishing the epidermis. The capillaries within the dermal papillae supply essential nutrients and oxygen to the epidermal cells, which are vital for cellular metabolism and regeneration. This nutrient exchange is particularly important for maintaining the skin's barrier function and promoting healing processes in response to injury or damage.
Sensory Perception
Dermal papillae are integral to the skin's sensory perception capabilities. The dense network of nerve endings within the dermal papillae allows for the detection of various stimuli, including touch, pressure, and temperature. This sensory feedback is crucial for the body's ability to interact with the environment and respond to potential threats.
Clinical Significance of Dermal Papillae
Impact on Hair Growth
Dermal papillae are closely associated with hair follicles and play a vital role in hair growth. The dermal papilla at the base of each hair follicle contains specialized cells that signal hair follicle development and cycling. These signals are essential for the regulation of the hair growth cycle, including the anagen (growth), catagen (transitional), and telogen (resting) phases.
Disruptions in the function of dermal papillae can lead to various hair disorders, such as androgenetic alopecia (pattern hair loss) and alopecia areata (patchy hair loss). Understanding the role of dermal papillae in hair growth has led to the development of targeted therapies aimed at stimulating hair follicle activity and promoting hair regrowth.
Skin Disorders and Conditions
Dermal papillae can also be affected by various skin disorders and conditions. For instance, conditions such as psoriasis and eczema can lead to inflammation and changes in the structure of dermal papillae, resulting in altered skin texture and function. Inflammatory processes can cause the dermal papillae to become enlarged or distorted, impacting their ability to support the epidermis and perform sensory functions effectively.
Furthermore, certain dermatological conditions can lead to the loss of dermal papillae, which may result in thinning skin and increased susceptibility to injury. Understanding the relationship between dermal papillae and skin disorders is crucial for dermatologists in diagnosing and treating various skin conditions effectively.
Research and Future Directions
Advancements in Dermatological Research
Ongoing research into the biology and function of dermal papillae is providing valuable insights into skin health and disease. Scientists are exploring the molecular mechanisms that regulate dermal papillae function and their role in hair follicle biology. This research is paving the way for innovative therapies aimed at addressing hair loss and other skin-related issues.
Additionally, advancements in regenerative medicine are focusing on harnessing the potential of dermal papillae to promote skin healing and regeneration. Techniques such as stem cell therapy and tissue engineering are being investigated as potential avenues for enhancing dermal papillae function and improving skin health.
Potential Therapeutic Applications
The understanding of dermal papillae's role in skin and hair health has significant implications for therapeutic applications. Treatments targeting the signaling pathways involved in dermal papillae function could lead to breakthroughs in managing hair loss and skin disorders. For instance, topical agents that stimulate dermal papillae activity may enhance hair follicle regeneration and improve hair density.
Moreover, the exploration of dermal papillae in the context of wound healing is an exciting area of research. By promoting the regeneration of dermal papillae, it may be possible to enhance the healing process in damaged skin and improve outcomes for patients with chronic wounds or surgical scars.
Conclusion
In summary, dermal papillae are essential structures within the skin that play a critical role in supporting the epidermis, facilitating nutrient exchange, and enabling sensory perception. Their significance extends beyond basic skin health, impacting hair growth and the manifestation of various skin disorders. As research continues to uncover the complexities of dermal papillae, the potential for innovative therapeutic applications grows, promising advancements in dermatology and skin care.
Understanding the anatomy, functions, and clinical significance of dermal papillae is vital for dermatologists and healthcare professionals as they strive to provide effective treatments and improve patient outcomes. The ongoing exploration of these structures will undoubtedly contribute to the future of dermatological science and the development of novel therapies for skin and hair conditions.
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology