Introduction to Mohs Surgery
Mohs surgery, named after Dr. Frederic Mohs who developed the technique in the 1930s, is a specialized surgical procedure used primarily to treat skin cancer. This innovative technique is designed to remove cancerous skin while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible. The unique aspect of Mohs surgery lies in its methodical approach to excising cancerous cells and its real-time microscopic examination, which allows for immediate assessment of the margins of the excised tissue.
The procedure is particularly effective for non-melanoma skin cancers, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which are the most common forms of skin cancer. Mohs surgery is often recommended for cancers located in cosmetically sensitive areas, such as the face, ears, and neck, where preserving healthy tissue is crucial for optimal cosmetic outcomes.
In this glossary entry, we will delve into the various aspects of Mohs surgery, including its indications, procedure, benefits, risks, and post-operative care, providing a comprehensive understanding of this vital dermatological technique.
Indications for Mohs Surgery
Mohs surgery is indicated for various types of skin cancers, particularly those that exhibit aggressive behavior or are located in challenging anatomical areas. The following are common indications for Mohs surgery:
- Non-Melanoma Skin Cancers: Mohs surgery is primarily used for basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which are the two most prevalent forms of skin cancer.
- Recurrent Skin Cancers: Patients with skin cancers that have recurred after previous treatments may benefit from Mohs surgery, as it allows for precise removal of cancerous tissue.
- Cancers in High-Risk Areas: Tumors located on the face, ears, scalp, and neck, where cosmetic outcomes are paramount, are ideal candidates for Mohs surgery.
- Large Tumors: Larger tumors may require Mohs surgery to ensure complete removal of cancerous cells while preserving surrounding healthy skin.
Additionally, Mohs surgery is often recommended for skin cancers that exhibit aggressive histological features, such as perineural invasion or a high likelihood of metastasis. The decision to proceed with Mohs surgery is typically made after a thorough evaluation by a board-certified dermatologist or Mohs surgeon.
The Mohs Surgery Procedure
Pre-Operative Preparation
Before undergoing Mohs surgery, patients are typically advised to avoid blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), for a few days prior to the procedure. This is to minimize the risk of excessive bleeding during surgery. Patients should also inform their surgeon of any medical conditions, allergies, or medications they are currently taking.
During the initial consultation, the Mohs surgeon will conduct a thorough examination of the skin cancer, discuss the surgical process, and explain the expected outcomes. Patients may also be asked to sign consent forms acknowledging their understanding of the procedure and its potential risks.
Step-by-Step Surgical Process
The Mohs surgery procedure typically involves the following steps:
- Anesthesia: The area surrounding the tumor is numbed using a local anesthetic to ensure patient comfort during the procedure.
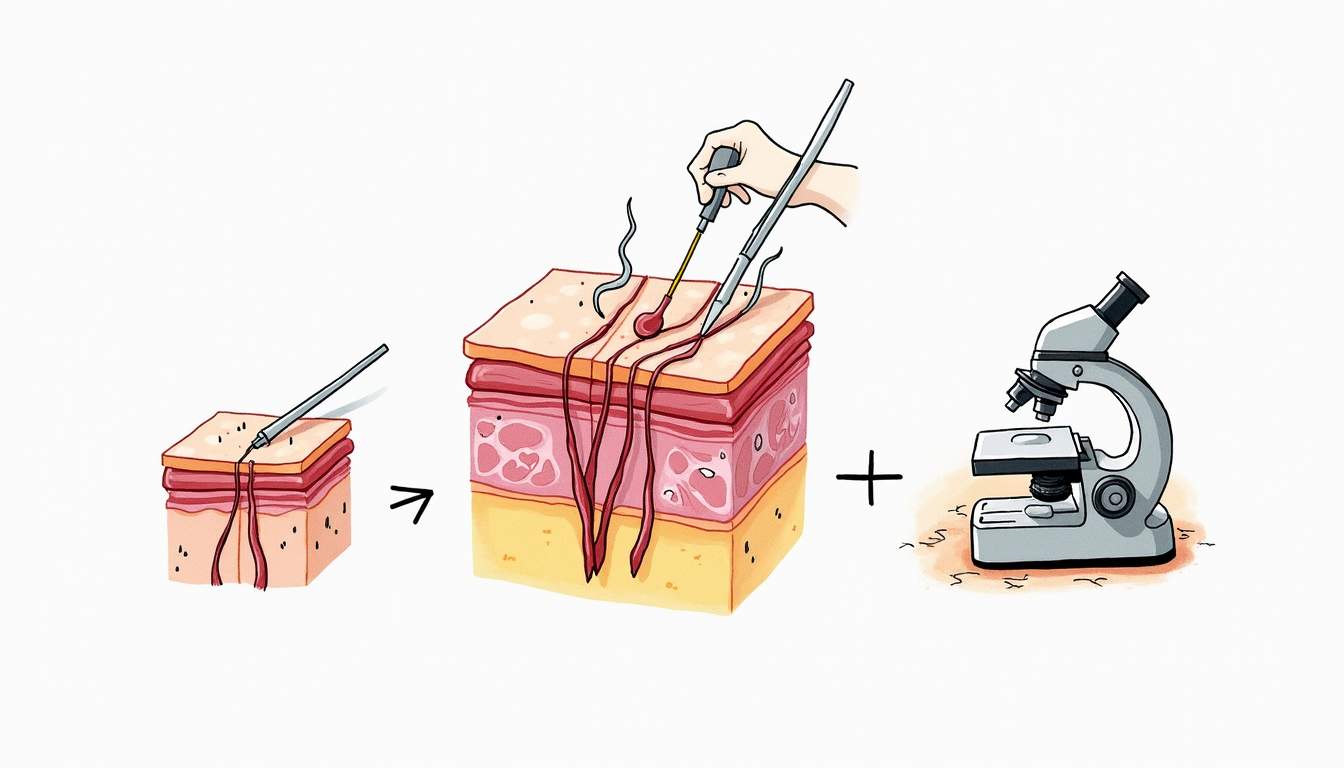
- Tumor Removal: The surgeon carefully excises the visible tumor along with a thin layer of surrounding skin. This layer is typically 1-2 millimeters thick.
- Immediate Microscopic Examination: The excised tissue is then processed and examined under a microscope to check for cancerous cells. This step is crucial as it allows for real-time assessment of the surgical margins.
- Further Excision if Necessary: If cancerous cells are detected at the margins, the surgeon will remove another layer of skin, repeating the examination process until clear margins are achieved.
- Closure: Once clear margins are confirmed, the surgeon will proceed to close the wound, which may involve suturing, skin grafting, or other techniques depending on the size and location of the excised area.
Benefits of Mohs Surgery
Mohs surgery offers several significant advantages over traditional surgical techniques for skin cancer removal. These benefits include:
- Maximized Tissue Preservation: The primary goal of Mohs surgery is to remove cancerous cells while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible, which is especially important in cosmetically sensitive areas.
- High Cure Rates: Mohs surgery boasts a cure rate of up to 99% for non-melanoma skin cancers, making it one of the most effective treatments available.
- Immediate Results: The real-time examination of excised tissue allows for immediate feedback, reducing the likelihood of needing additional surgeries.
- Minimized Scarring: By preserving healthy skin, Mohs surgery often results in less scarring and improved cosmetic outcomes compared to traditional excisional surgery.
Risks and Considerations
While Mohs surgery is generally considered safe, like any surgical procedure, it carries certain risks and potential complications. Patients should be aware of the following:
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a risk of infection at the surgical site. Proper post-operative care and hygiene can help mitigate this risk.
- Bleeding: Some bleeding is expected during and after the procedure, but excessive bleeding may require additional intervention.
- Scarring: Although Mohs surgery aims to minimize scarring, some patients may still experience noticeable scars, particularly if the tumor was large or located in a challenging area.
- Recurrence: While Mohs surgery has high cure rates, there is still a possibility of recurrence, especially if the cancer was aggressive or if the patient has a history of skin cancer.
Patients should discuss their individual risk factors and concerns with their Mohs surgeon prior to the procedure to ensure they have a comprehensive understanding of what to expect.
Post-Operative Care
After Mohs surgery, proper post-operative care is essential for optimal healing and cosmetic outcomes. Patients are typically given specific instructions, which may include:
- Wound Care: Patients should keep the surgical site clean and dry, following any specific wound care instructions provided by their surgeon.
- Pain Management: Mild discomfort is common after the procedure, and patients may be advised to take over-the-counter pain relievers as needed.
- Activity Restrictions: Patients may be advised to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, or swimming for a specified period to allow the wound to heal properly.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Regular follow-up appointments may be scheduled to monitor healing and assess for any signs of recurrence.
Conclusion
Mohs surgery is a highly effective and specialized technique for treating skin cancer, particularly in sensitive areas where cosmetic outcomes are a priority. Its unique approach of real-time microscopic examination ensures that cancerous cells are thoroughly removed while preserving healthy tissue, leading to high cure rates and minimal scarring. Understanding the indications, procedure, benefits, risks, and post-operative care associated with Mohs surgery is essential for patients considering this treatment option. As always, patients should engage in open communication with their healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding their skin cancer treatment.
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology