Introduction to Lymphatic Drainage
The lymphatic system is a critical component of the body's immune system and plays a vital role in maintaining fluid balance, transporting nutrients, and removing waste products. Lymphatic drainage refers to the process by which lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, is transported through the lymphatic vessels to be filtered by the lymph nodes before returning to the bloodstream. In dermatology, understanding lymphatic drainage is essential for diagnosing and treating various skin conditions, as well as for enhancing the overall health of the skin.
Lymphatic drainage is particularly important in the context of dermatology because it helps to manage skin conditions that involve inflammation, swelling, or infection. Conditions such as lymphedema, psoriasis, and dermatitis can benefit from therapeutic techniques aimed at promoting lymphatic flow. By improving lymphatic drainage, dermatologists can help alleviate symptoms, enhance healing, and improve the overall appearance of the skin.
This glossary entry will explore the anatomy and physiology of the lymphatic system, the mechanisms of lymphatic drainage, its importance in dermatology, and various therapeutic techniques used to enhance lymphatic function.
Anatomy of the Lymphatic System
Components of the Lymphatic System
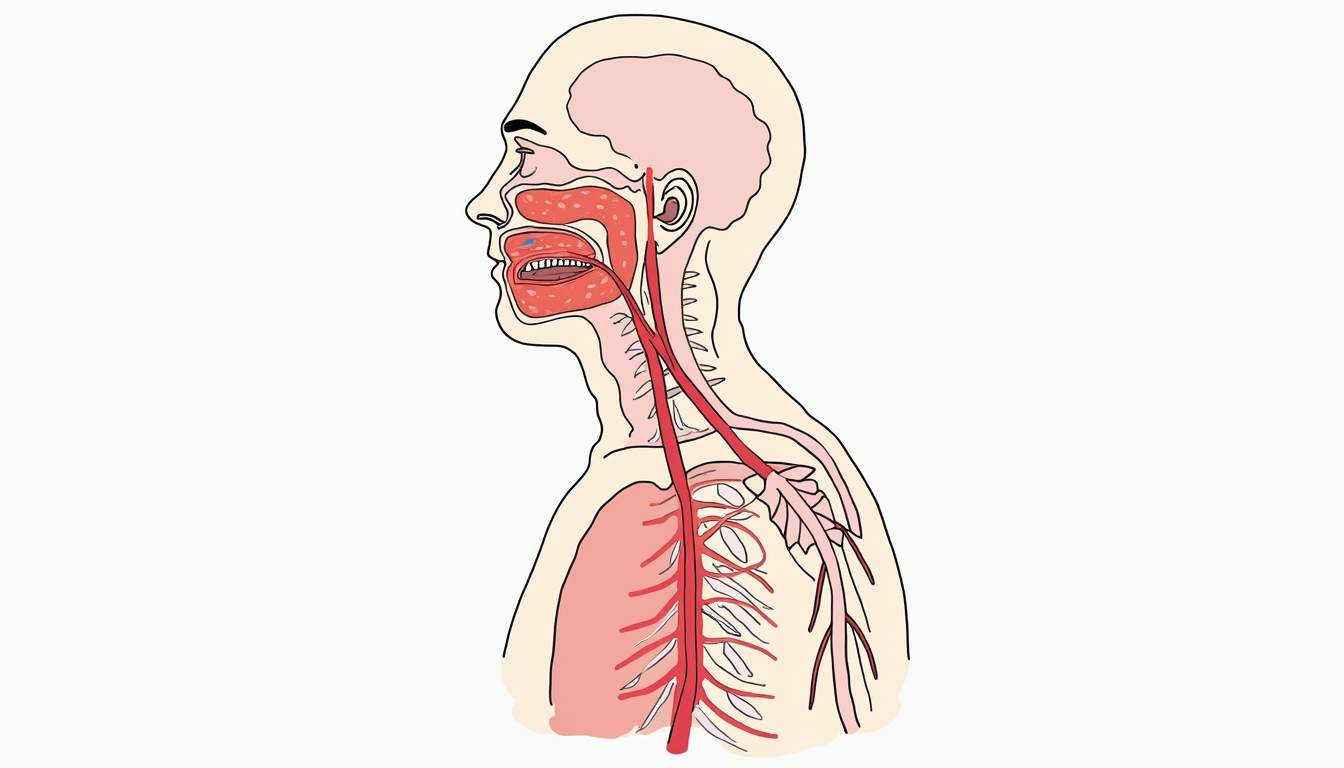
The lymphatic system consists of a network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and lymphoid organs. Lymphatic vessels are thin-walled tubes that transport lymph throughout the body. These vessels are similar to veins but have a more permeable structure, allowing them to absorb excess interstitial fluid, proteins, and waste products from tissues.
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph as it passes through them. They contain immune cells, such as lymphocytes and macrophages, which help to identify and eliminate pathogens and foreign substances. Major clusters of lymph nodes are located in the neck, armpits, and groin, and they play a crucial role in the immune response.
Functions of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system serves several essential functions in the body, including:
- Fluid Balance: The lymphatic system helps to maintain fluid balance by collecting excess interstitial fluid and returning it to the bloodstream, preventing edema and swelling.
- Immune Response: Lymph nodes filter lymph and house immune cells that respond to infections and foreign substances, playing a critical role in the body's defense mechanisms.
- Nutrient Transport: The lymphatic system transports dietary lipids and fat-soluble vitamins from the intestines to the bloodstream, facilitating nutrient absorption.
Mechanisms of Lymphatic Drainage
How Lymphatic Drainage Works
Lymphatic drainage occurs through a combination of intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms. Intrinsically, lymphatic vessels have smooth muscle in their walls that contracts rhythmically, propelling lymph forward. Additionally, the presence of one-way valves within the vessels prevents backflow, ensuring that lymph moves in the correct direction toward the thoracic duct, where it drains into the bloodstream.
Extrinsic factors that aid lymphatic drainage include skeletal muscle contractions during movement and respiration. When muscles contract, they compress nearby lymphatic vessels, facilitating the movement of lymph. Deep breathing also creates pressure changes in the thoracic cavity, promoting lymph flow. This interplay between intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms is vital for maintaining effective lymphatic drainage.
Factors Affecting Lymphatic Drainage
Several factors can influence lymphatic drainage, including:
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise enhances lymphatic flow by promoting muscle contractions that compress lymphatic vessels.
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake is essential for maintaining optimal lymphatic function, as dehydration can lead to thickening of lymph and impaired drainage.
- Posture: Certain postures can compress lymphatic vessels and impede drainage, while others can facilitate it. For example, elevating the legs can promote lymphatic return from the lower extremities.
Importance of Lymphatic Drainage in Dermatology
Role in Skin Health
Lymphatic drainage plays a significant role in maintaining skin health by facilitating the removal of waste products, toxins, and excess fluid from the skin's interstitial spaces. This process helps to prevent the accumulation of harmful substances that can lead to skin irritation, inflammation, and various dermatological conditions.
Moreover, effective lymphatic drainage supports the delivery of immune cells to the skin, enhancing the skin's ability to respond to infections and injuries. By promoting a healthy immune response, lymphatic drainage can help prevent skin infections and accelerate the healing process following skin trauma.
Impact on Dermatological Conditions
Several dermatological conditions can be positively influenced by improved lymphatic drainage, including:
- Lymphedema: A condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid, often resulting from surgery, radiation, or infection. Lymphatic drainage techniques can help reduce swelling and improve skin integrity.
- Psoriasis: An autoimmune condition that leads to rapid skin cell turnover and inflammation. Enhancing lymphatic drainage may help reduce inflammation and improve the overall appearance of the skin.
- Dermatitis: Inflammatory skin conditions that can benefit from improved lymphatic flow to reduce swelling and promote healing.
Therapeutic Techniques for Enhancing Lymphatic Drainage
Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a specialized massage technique designed to stimulate lymphatic flow and promote drainage. Practiced by trained therapists, MLD involves gentle, rhythmic movements that encourage lymph to move through the vessels and nodes. This technique is particularly beneficial for individuals with lymphedema or those recovering from surgery.
MLD can also be used as a complementary therapy for various skin conditions, helping to reduce swelling, improve circulation, and enhance the overall health of the skin. The technique is typically performed in a series of sessions, tailored to the individual's specific needs and conditions.
Compression Therapy
Compression therapy involves the use of specialized garments or bandages to apply pressure to affected areas, promoting lymphatic drainage and reducing swelling. This technique is commonly used in conjunction with MLD for patients with lymphedema or chronic venous insufficiency.
Compression garments are designed to provide graduated pressure, with the highest pressure at the extremities and gradually decreasing pressure as it moves up the limb. This design helps to facilitate lymphatic flow and prevent the accumulation of fluid in the tissues.
Conclusion
In summary, lymphatic drainage is a crucial aspect of dermatology that plays a significant role in maintaining skin health and managing various dermatological conditions. By understanding the anatomy and physiology of the lymphatic system, the mechanisms of lymphatic drainage, and the therapeutic techniques available to enhance lymphatic function, dermatologists can provide comprehensive care that addresses not only the symptoms of skin conditions but also their underlying causes.
As research continues to evolve in the field of dermatology, the importance of lymphatic drainage will likely become increasingly recognized, leading to more innovative treatment approaches that leverage the body's natural systems for improved skin health.
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Visit Our Offices
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology
Services:
- • Medical Dermatology
- • Surgical Dermatology
- • Laser Treatments
- • Cosmetic Dermatology